You are here: / Home
American Institute of Physics publishes a microscopic image taken at the ILK Dresden
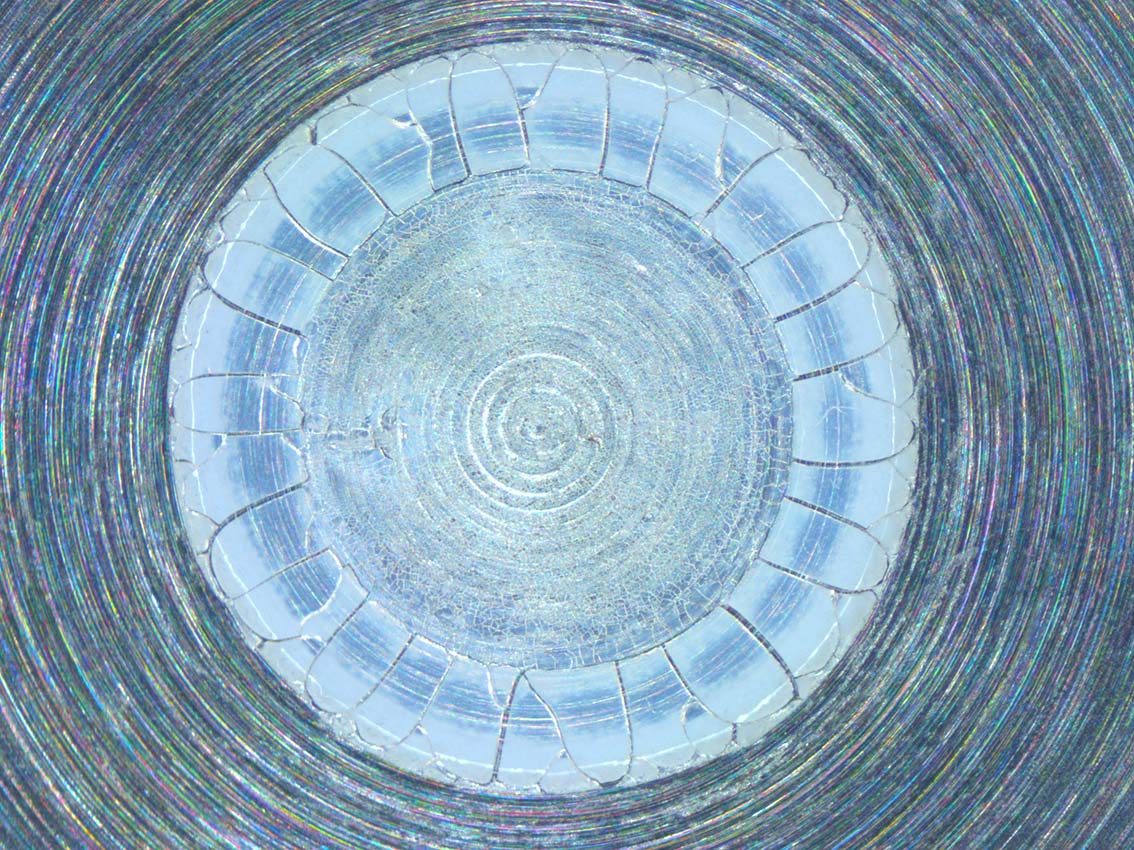
Only extraordinary images make it onto the title of “Physics Today”.
Physics Today 74, 8, 64 (2021); https://doi.org/10.1063/PT.3.4823
This microscopic image now belongs to this category.
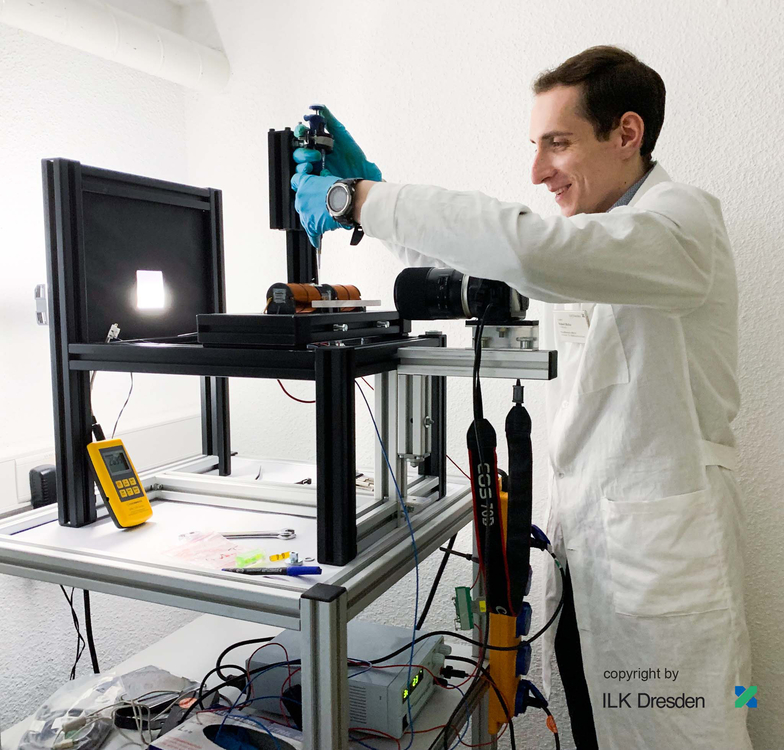
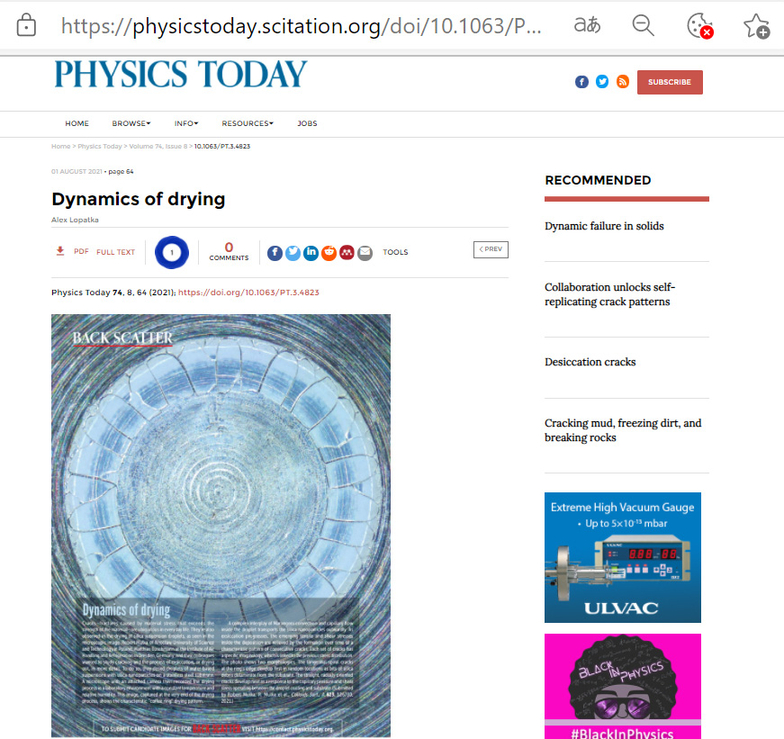
It emerged in cooperation with the University of Science and Technology Wrocław (Poland) and the University of Padova (Italy) under the lead of Robert Mulka (UoW) and Matthias H. Buschmann (ILK Dresden). They microscopically filmed the drying process of a ten-microliters droplet of a silicon dioxide suspension. At the end of the process, the characteristic coffee-ring pattern with a diameter of ca. 3 mm, known from dried tea or coffee drops, became visible. The goal of the study had been to better understand the formation of nanoporous coating of vaporizer surfaces, e.g. in thermal syphons.
Cracks are ubiquitous in everyday life. Their sizes vary over several magnitudes, from 500 μm as in the examined droplet, up to the 140 km long crack in the Larsen C Ice Shelf in Antarctica discovered in 2017.
Robert Mulka, Matthias H. Buschmann and their colleagues set out to examine crack formation and the process of drying out further. For that purpose, they dispensed droplets of an aqueous silicon dioxide suspension (particle size ca. 70 nm) into two different metallic substrates. A microscope with an attached camera recorded the drying process under lab conditions.
The image published shows the final stage of the drying process with complete crack formation. The coffee ring and the radial cracks are clearly visible. The outer edge of the droplet shows tangential spiral cracks, which appear first and induce the massive radial cracks.
The interplay of Marangoni convection, driven by the gradients of the droplet’s surface tension, and the capillary flow inside the droplet transports the silicon dioxide particles to the edge and thereby forms the coffee ring in the silicon dioxide coating.
During the process of further drying out, tensile and sheer stress forms, which is then relieved when cracks appear. The shape of the cracks depends on the local stress distribution. Spiral cracks first appear in random places on the edge when parts of the silicon dioxide coating detach from the substrate. The radial cracks are result of the interaction between capillary stress and sheer stress between the silicon dioxide layer and the substrate.
(Mulka et al., 623, (2021) 126730, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126730).