You are here: Home / Research and Development
Investigation of material-dependent parameters
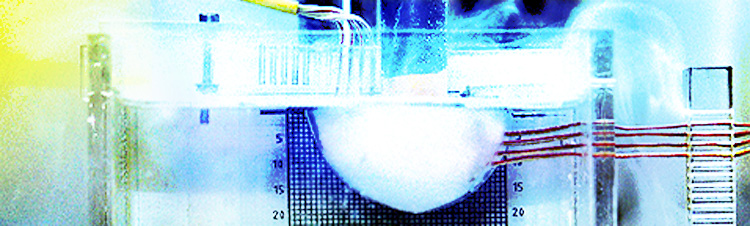
Investigation of the permeation behavior
Permeation is the penetration of solid matter by another substance. The driving force for this is a gradient of the chemical potential of the permeate. In practice, this gradient is replaced by a measurable quantity such as the pressure gradient. The permeability of a material depends on the surface temperature and is usually specified with the unit \( \frac{\mu g}{cm^2\:min} \)
Without external influences, the permeate always moves in the direction of the lower concentration or the lower partial pressure. For theoretical consideration, permeation can be divided into three sections across the solid:
- Sorption, for example, a gas is absorbed at the surface of the solid
- Diffusion, this gas diffuses through the solid through molecular gaps towards the surface with a lower gas concentration
- Desorption, the gas is released again from this surface
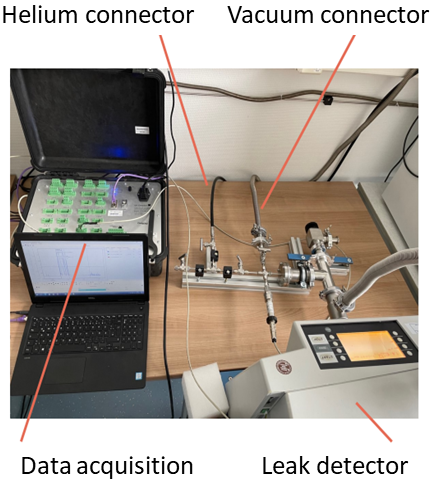
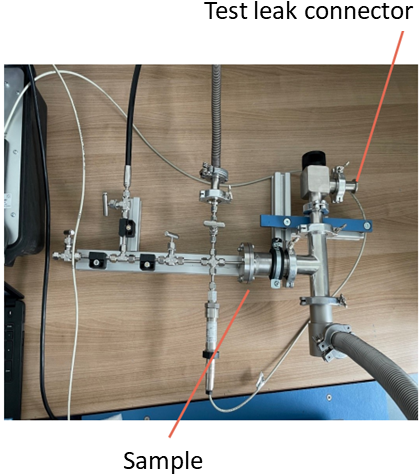
The experimental setup to investigate this process, see the following figures, essentially consists of a sample chamber. The sample is mounted with a seal or against a sealing surface. A test gas with a defined overpressure is applied to the volume on the "left" of the sample. The volume to the "right" of the sample is connected to a detector. The pressure on both sides of the sample, the temperatures and the gas flow rate are measured over a longer period of time (24 - 48 h).
| Parameter | Sample limits |
|---|---|
| materials | plastics, metals |
| dimensions, diameter, and wall thickness | 58 ... 60 mm, 1 ... 3 mm other dimensions on request |
| pressure difference | up to 10 bar (145 psi) |
| temperature range | room temperature, other conditions on request |
| test gas | helium or hydrogen |
| detector measuring range | up to \(10^{-9} \frac{mbar\:l}{s} \), optional with calibration |
Your Request
Further Projects - Research and Development
Hydrogen and methane testing field at the ILK
Simultaneously pressures up to 1,000 bar, temperatures down to –253°C
Low noise and non metallic liquid-helium cryostat
Low-noise Magnetic Field Cryostat for SQUID-Applications
Cryostats, Non-Metallic and Metallic
position indenpendent, highest endurance, tiltable for liquid helium and liquid nitrogen
Cryogenic liquid piston pumps for cold liquefied gases like LIN, LOX, LHe, LH2, LNG, LAr
Feeding pumps for cryogenic liquid gases