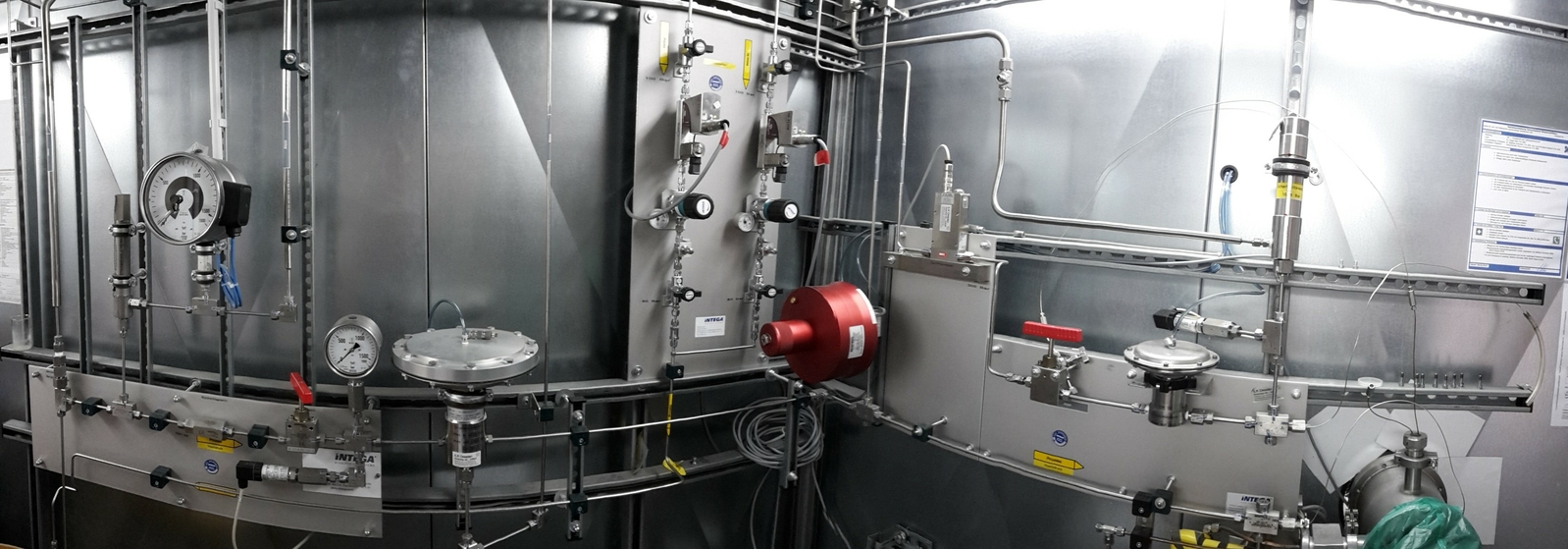
- Test and qualification of components at temperatures ranging from 20 K (−253 °C) to room temperature and pressures ranging from high vacuum to 1000 bar (e.g. test of sealings, permeation tests).
- Investigation of charge and discharge processes at cryogenic or room-temperature-operated storage systems for hydrogen and methane (e.g. adsorber storage systems, cryo-compressed hydrogen).
- Investigation of catalyst materials for the ortho–para conversion of hydrogen.
- Long-time thermal charging of components and materials in hydrogen or methane atmosphere at up to +200 °C and up to 160 bar for investigating degradation effects (e.g. hydrogen embrittlement).
- Development of different hydrogen and methane components (e.g. recooling systems, latent-heat storage systems, cryogenic pressure storage systems, heat exchangers, cryogenic pumps).
- Realisation of complete-system solutions for hydrogen and methane.
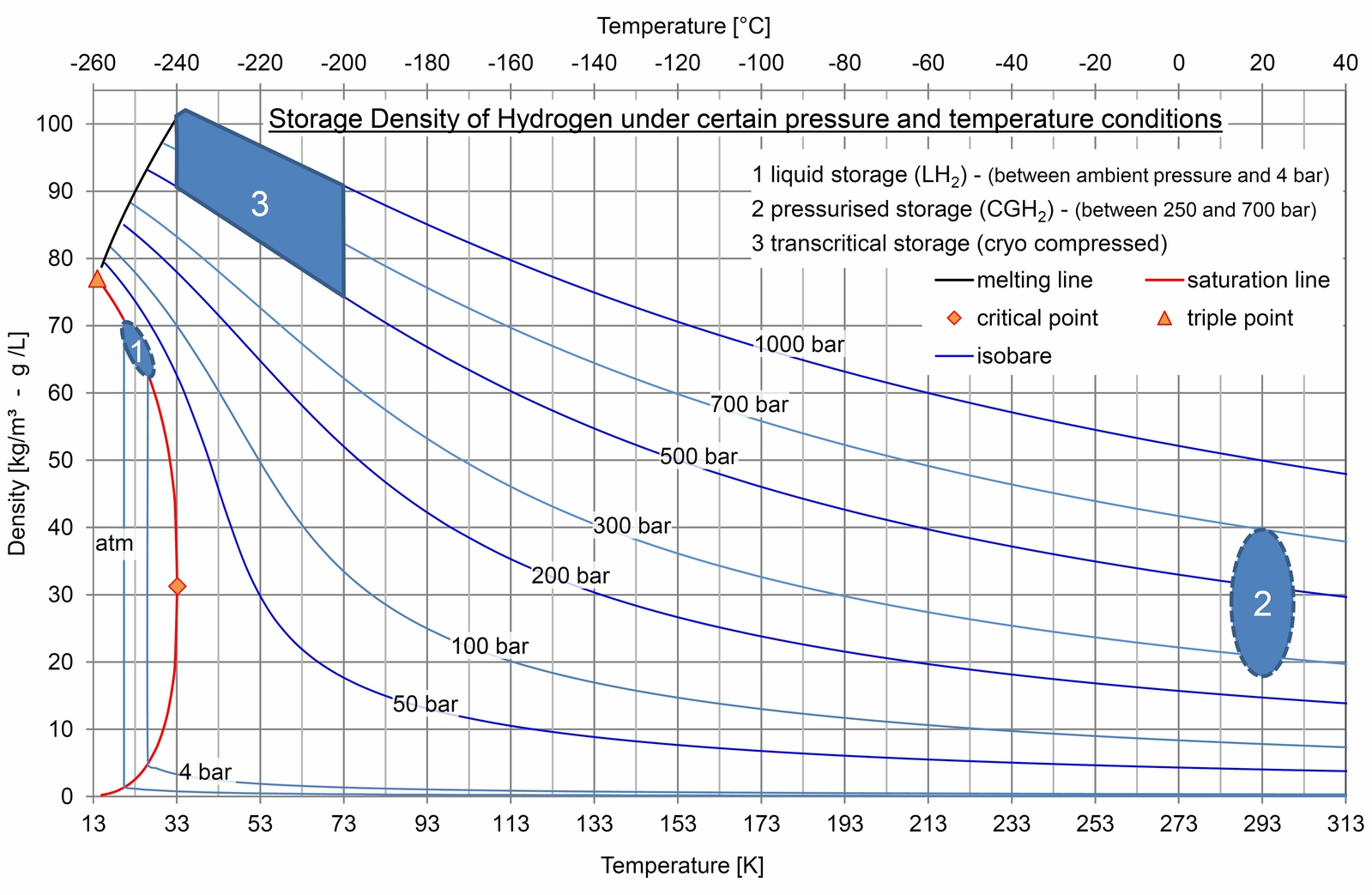
The following diagram depicts the specific storage density that can be achieved depending on temperature and pressure: