You are here: / Home
Test method for high - temperature heat pump - oils

PrüVeÖl
Short description:
High-temperature heat pumps can make an important contribution to decarbonization. Their market acceptance requires validated data on the thermodynamic and chemical properties of the lubricating oils in a mixture with refrigerant for temperatures up to 190 °C (compressor end temperature). The equipment and methods required for this data are not yet available (state of the art max. 140 °C) and are to be designed, constructed and tested as part of the project.
Objective:
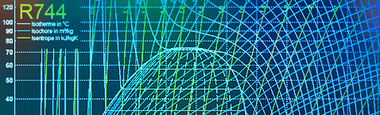
The project focuses on the development of methods, equipment and measurement setups for determining the thermodynamic properties of refrigerant-oil mixtures (LMEO) in the elevated temperature range up to 190 °C (30 K above the sink temperature of 160 °C). In order to describe the behavior of MWFOE in the compressors of the heat pumps, their mixing behavior, vapor pressure, density and viscosity are primarily required - in each case as a function of temperature and pressure.
The maximum pressures depend on the operating temperature and the pressure level of the refrigerant used. From the range of natural refrigerants, hydrocarbons (HC), R744 (CO2), R717 (NH3) and R718 (water) are suitable for heat pumps. For the common HC refrigerants, pressures of at least 40 bar are achieved. For R744, R717 and R718, pressures of up to 200 bar can be expected.
The project also aims to develop methods for investigating the stability and compatibility of MWF refrigerants with materials and substances for use up to 190 °C. The methods should enable a valid statement to be made on the long-term resistance (service life) without destroying the MWPE or materials by excessive temperature increases (false negative test). It should be possible to make a statement within an acceptable period of time (usually 1 week to max. 6 weeks).
This results in the following objectives:
- Development, construction and testing of a measuring cell for determining the miscibility gap between refrigerant and oil up to 190 °C and 200 bar
- Development, construction and testing of a measuring cell for measuring the vapor pressure of refrigerant-oil mixtures up to 190 °C and 200 bar
- Development, construction and testing of a density measuring station for refrigerant-oil mixtures up to 190 °C and 200 bar
- Development, construction and testing of a measuring station for measuring the viscosity of refrigerant-oil mixtures up to 190 °C and 200 bar
- Development of a process including the construction of the associated apparatus for determining the long-term chemical stability of the VHTHP oil together with the refrigerant (for final compression temperature up to 190 °C)
- Development of a process, including construction of the associated apparatus, to determine the long-term chemical compatibility of VHTHP materials together with oil and refrigerant (for final compression temperature up to 190 °C)
For the natural refrigerants favored by science and politics for heat pumps, special safety requirements must be provided for these new processes and equipment with regard to flammability (KW), toxicity (e.g. R717) and corrosiveness (e.g. R718). Special attention should therefore be paid to small sample volumes and technical safety functions of the equipment.
Further Projects
Tensile and compression testing
Determination of yield strength, tensile strength and elongation at break
Breakthrough Sensor for Adsorption Filters (BelA)
Sensor system for detecting an imminent breakthrough in gas filtration