You are here: Home / Research and Development
Refrigerants, lubricants and mixtures

Determination of working fluid properties
Investigations of refrigerants, oils and its mixtures
On base of our great database and knowledge ILK offer consulting services to choose the right refrigerant-lubricant system for special purposes. Following you will find a selection of applicable determination methods to qualify working fluid.
Floc point
Standard: | DIN 51351 |
Instrument: | Pressure proof autoclave with elongate glasses, cooling bath |
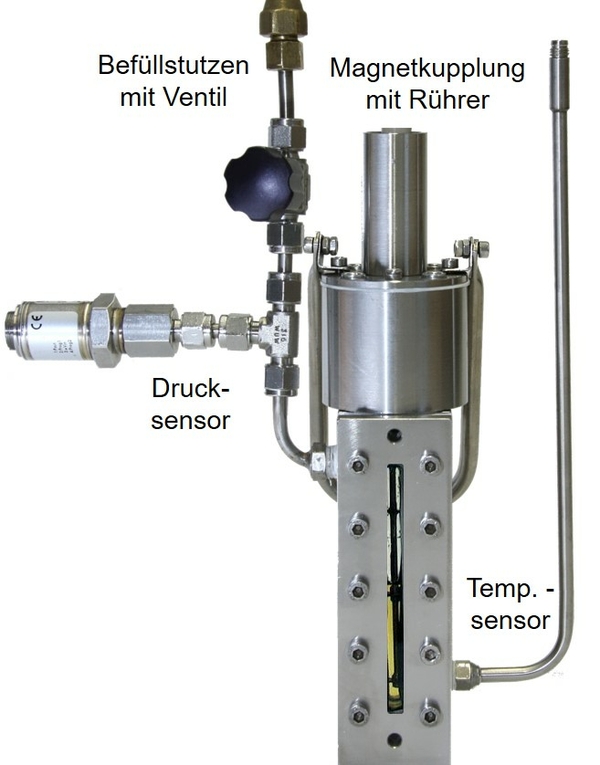
Principle: | The refrigerant-oil mixture with defined weight fraction (10 wt% oil) is cooled down in a pressure proof autoclave with elongate glasses (see picture 1), until flocs appear at a defined temperature. The cloud point is dependent from the concentration of the refrigerant-oil mixture. |
Temperature range: | –60 °C to room temperature |
| Pressure range: | 1 to 70 bar |
Amount of sample required: | 10 ml |
Modifications: | Nebula Test (5 wt% oil), Cloud point of immiscible fluids ( = with oil saturated refrigerants) |
| [top:nach oben] |
Solidification Point / Pour Point
Standard: | DIN EN ISO 3016:2019 |
Instrument: | Test vessel according to specified DIN EN ISO, cryostat cooling bath |
Principle: | The liquid to be tested is cooled down until the liquid is no more free-flowing at a defined temperature. |
Temperature range: | –60 °C to room temperature |
Amount of sample required: | 250 ml |
| [top:nach oben] |
Miscibility Gap
Standard: | DIN 51514 |
Instrument: | Pressure proof autoclave with elongate glasses, cooling bath |
Principle: | The segregation line between one and two phase of refrigerant-oil mixtures is determined in dependency of the concentration, both at high and low temperatures. |
Temperature range: | –60 °C to 140 °C |
| Pressure range: | 1 to 70 bar |
Amount of sample required: | 250 ml |
| [top:nach oben] |
Specific heat capacity
Standard: | ASTM D 3947 or E 1269 |
Instrument: | Differential scanning calorimeter Setaram µDSC7 evo or Differential scanning calorimeter TA Instruments Q200 |
Principle: | Thermal effects of the sample can be detected in dependence of temperature and time by continuous heating, cooling or isothermal operation mode and comparing with a reference. For instance these effects can be freezing, melting, phase changing effects, chemical reaction and so on. |
Temperature range: | -45 °C to 90 °C in the pressure range up to 20 bar -180 °C to 750 °C at normal pressure up to 200 bar |
Pressure range: | 1 to 200 bar |
Sensitivity: | 0,2 µW |
Amount of sample required: | 10 ml |
| [top:nach oben] |
Thermal conductivity
Instrument: | test cell for stationary cylinder gap method |
Principle: | The coolant to be measured is placed in a gap between a heatable inner and an outer cylinder. The inner cylinder is heated with a defined rate. After the heat flow is stationary the temperature difference of the liquid in the gap is measured with Pt100 temperature sensor. |
Temperature range: | -40 °C to 140 °C |
Pressure range: | 1 to 100 bar |
Measurement range: | 50 to 200 mW · m–1 · K–1 |
Amount of sample required: | 250 ml |
| [top:nach oben] |
Vapor pressure
Instrument: | Test cell for determination of vapor pressure (500 cm3) |
Principle: | The measurement of the vapor pressure allows conclusions on the liquid solubility of the refrigerant in refrigeration oil. The refrigerant-oil mixture is made gravimetric direct in the measuring cell (picture 2). This cell is tempered and the vapor pressure is determined with direct method. |
Temperature range: | -60 to 90°C |
Pressure range: | 1 to 130 bar |
Amount of sample required: | 500 ml |
| [top:nach oben] |
Density
Standard: | DIN 51757 |
Instrument: | Oscillating U-tube density meter DPR 412 Y / DMA 60 (Anton Paar) |
Principle: | A defined volume of the sample is filled into a U-shaped tube which is electronically excited into undamped oscillation. The eigenfrequency of this U-tube is depending on the mass of the sample. The density is calculated from the frequency of the oscillation. |
Temperature range: | -10 °C to 140 °C |
Pressure range: | 1 to 160 bar |
Measurement range: | 600 to 1300 kg · m–3 |
viscosity: | < 15.000 mm2 · s-1 |
Amount of sample required: | 250 ml |
| [top:nach oben] |
Dynamic / Kinematic viscosity
Standard: | ASTM D 7483 |
Instrument: | Oscillating piston viscometer (Cambridge Viscosity) |
Principle: | Oscillating piston viscometers allow dynamic viscosity measurement of a broad range of materials including transparent, translucent and opaque liquids. The measurement principle and stainless steel construction makes the Oscillating Piston Viscometer resistant to damage and suitable for portable operations. Kinematic viscosity is calculeted from dynamic viscosity with the density. |
Temperature range: | -40 to 140 °C |
Pressure range: | 1 to 160 bar |
Measurement range: | 0,2 to 20.000 mPa · s |
Amount of sample required: | at least 10 ml |
| [top:nach oben] |
Dielectric constant - Permittivity
Standard: | ASTM D 924 – 04; DIN IEC 247 |
Instrument: | Pressure proof measuring cell for measuring electrical properties (selfmade) |
Principle: | The test liquid or the mixture of refrigerant and refrigeration oil is placed in an annular gap. Inner cylinder and outer cylinder are used as electrodes. The measuring cell can be tempered. The permittivity, the alternating current resistance and the dissipation factor are measured at standard conditions of 1 V and 1kHz. |
Temperature range: | -20 to 100 °C |
Pressure range: | 1 to 140 bar |
Measurement range: | 1 to 20 |
Amount of sample required: | 250 ml |
| [top:nach oben] |
Direct current of insulating liquids
Standard: | ASTM D 1169 – 02; DIN IEC 247 |
Instrument: | Pressure proof measuring cell for measuring electrical properties (selfmade) |
Principle: | The test liquid or the mixture of refrigerant and refrigeration oil is placed in an annular gap. Inner cylinder and outer cylinder are used as electrodes. The measuring cell can be tempered. The direct current resistance can be determined with an exposure from 1 to 500 V and 3 mA to 0,1 pA (10-12 A). |
Temperature range: | -20 to 100 °C |
Pressure range: | 1 to 140 bar |
Measurement range: | 1 kW – 1,6 TW |
Amount of sample required: | 250 ml |
| [top:nach oben] |
DSC Measurements
Standard: | several |
Instrument: |
Differential scanning calorimeter Setaram µDSC VII or Differential scanning calorimeter TA Instruments Q200 |
Methods: | Besides the measurement of heat capacity of solids and fluids following material parameter are measurable with differential scanning calorimetry at the ILK:
|
Temperature range: | -40 °C to 750 °C |
Pressure range: | 1 bar (whole temperature range); 1 to 100 bar (-45 to 90 °C) higher pressures or temperatures on request |
Amount of sample required: | 1 ml or 1 mg |
| [top:nach oben] |
Further measurements (for instance neutralization number (TAN, TBN), speed of sound, surface tension) can be arranged on request.
Your Request
Further Projects - Research and Development
Optimizing HVAC operation with machine learning
Intelligent control of HVAC systems – high comfort with low energy demand
Industry 4.0 membrane heat and mass exchanger (i-MWÜ4.0)
Linking the entire life cycle of a multi-functional air handling unit