You are here: Home / Software Development
Overall System Optimization of Refrigeration Plant Systems for Energy Transition and Climate Protection

GOKAS
Subproject: Fault simulation, detection and diagnosis
Within the joint project GOKAS, the ILK Dresden is dedicated to the topics of fault generation, detection and diagnosis. Using machine learning methods, plant monitoring for field plants, especially in the field of commercial refrigeration, is to be raised to a new level.
The aim is to detect malfunctions in the operation of refrigeration systems before they lead to a loss of efficiency or system failure. For this purpose, process data will be evaluated with innovative technologies (e.g. machine learning) in order to automatically distinguish fault-free plant operation from disturbed operation.
For this purpose, error-free operating data is initially generated on a laboratory system and successively underlaid with errors in subsequent project steps by means of various manipulations. The error detection is to be implemented with suitable machine learning methods; the potential of neural networks is used for this. In the course of the development, suitable AI models for plant monitoring will be sought and their effectiveness tested. The programming environment and libraries required for the development are primarily based on Python. The aim is to detect deviations in the operation of the plants (parameter comparison, plant drift, ...). Prognoses are to enable a model-based process analysis as an additional option in order to differentiate between faulty and fault-free plant operation. The training data sets required for the development come in a first step from the laboratory plant. For a strong practical relevance, operating data from field plants will be included in the model development in subsequent project steps, thus expanding the spectrum of monitoring scenarios.
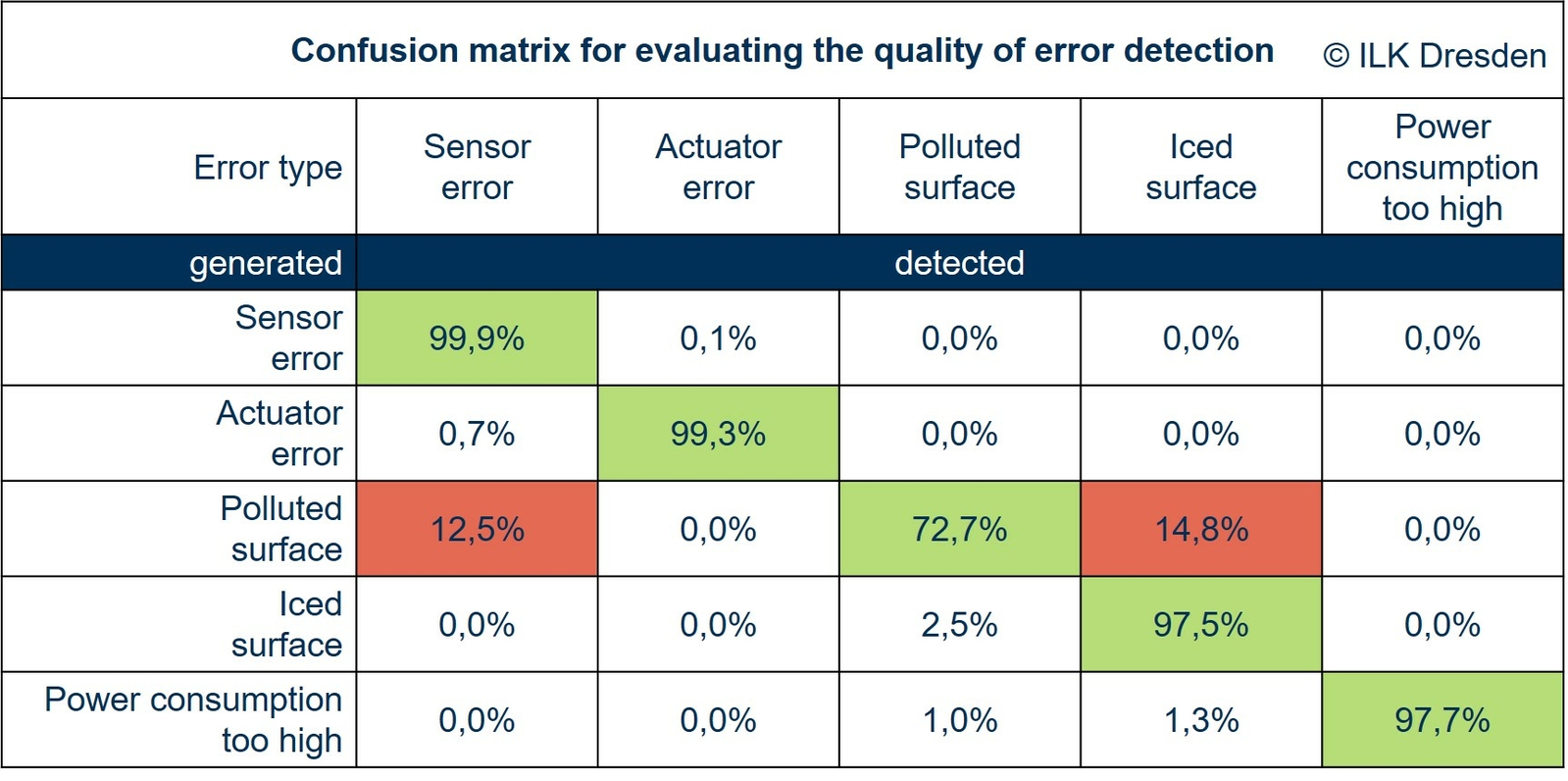
In the current project phase, good/bad data from different operating states of the laboratory plant are generated. These data are combined with different AI models and tested for the detection of operating conditions. The focus of the current investigations is to determine appropriate observation periods for monitoring, the architecture of the AI model to be applied, the quality of recognition of an operating condition, and the time spent learning the model for this purpose. These parameters will be iteratively modified to achieve high practicality.
Confusion matrix for evaluating the quality of error detection
The GOKAS joint project is an example of cross-thematic collaboration between various research partners with the aim of advancing innovative approaches to digitization (e.g., data mining, data science) and computational intelligence in the application field of air conditioning and refrigeration technology, thereby supporting the digital energy transition.
Biberach University of Applied Sciences is the research coordinator of the project and, in addition to indirect energy efficiency assessment, is concerned with the flexibility and load management of refrigeration systems. BUILD.ING Consultants + Innovators GmbH from Nuremberg is responsible for the core objective of energy-optimized building operation by applying machine learning methods. The fourth partner involved in the project is Trevisto AG from Nuremberg, an IT specialist for data science applications. Trevisto is responsible for data integration, model design and system integration for the AI/ML workflow in the project.
Partner:
Hochschule Biberach, Institut für Gebäude- und Energiesysteme (IGE)
https://www.hochschule-biberach.de/gokas
BUILD.ING Consultants + Innovators GmbH
TREVISTO AG
https://www.trevisto.de/forschung/gokas/