You are here: / Home
Innovative Manufacturing Technologies for Cryosorption Systems
Vacuum Pumps for UHV and XHV
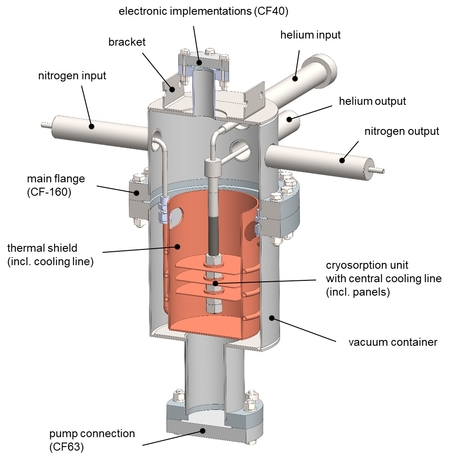
A cryosorption system is defined as a vacuum pump that captures gas on cryogenic surfaces (gas-binding vacuum pump). Thus pressures lower than 5-12 mbar are obtainable (realisation of UHV - ultrahigh vacuum and XHV - extremely high vacuum). Cryosorption systems rely on very good heat transfer performance. This is currently being achieved with a complex, cost-intensive and risky manufacturing process. Therefore the aim of this project is to develop a new manufacturing technology that does not have this disadvantage.
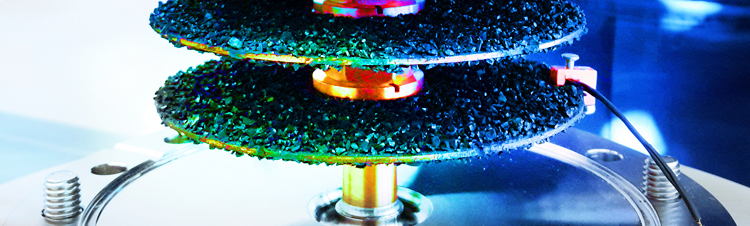
For this purpose, thermodynamically important variables, such as sorption heat and heat transfer resistance were determined mathematically. A test sample was developed and constructed based on these results.
After completion of the design the test sample will be produced.
In the further course of the R&D project a test stand will be set up on which the test sample can be measured. These measurements will be checked and validated in a CFD simulation. With the help of the CFD model, various simulations for future cryosorption systems can be carried out. For example cooling times for different activated carbon masses or the thermal performance under different conditions for the cooling medium can be determined using this method.
Finally the sample production (functional sample) of a cryosorption system made of stainless steel with a precisely defined heat transfer behaviour takes place. The functional model is measured in relation to the cooling performance and pressure loss of the cooling medium and the results obtained will be included into the creation of a process instruction for manufacturing future cryosorption systems.
Further Projects
All-in-one device for freeze-drying and production of biomaterial
with automated freezing and sterilisation option
Certification of efficient air conditioning and ventilation systems through the new "indoor air quality seal" for non-residential buildings
Good news for building owners, architects, general contractors and specifiers:
Investigation according to DIN EN ISO 14903
These tests according to DIN EN ISO 14903 are possible at ILK Dresden