You are here: Home / Research and Development
Ionocaloric cooling
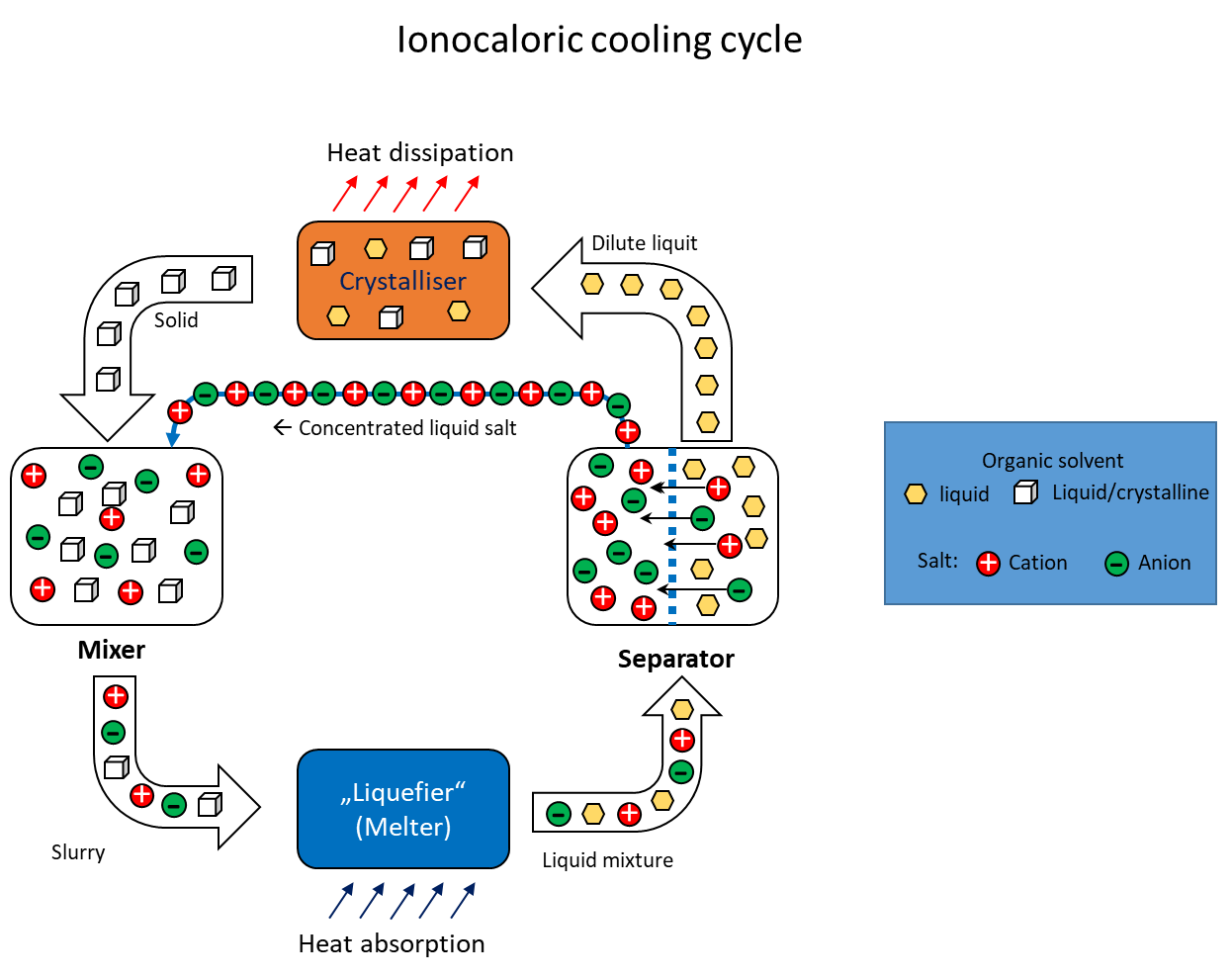
Ionocaloric solid-liquid phase cooling process
The utilisation of caloric effects for refrigeration purposes has been investigated and discussed for several years. Caloric effects in solids result from complex interactions between their atomic or molecular structures, which are influenced by mechanical pressure, magnetic fields or electric fields. The potential future utilisation of these caloric effects could drive the development of refrigeration systems that are characterised by higher energy efficiency and environmental friendliness than conventional cooling technologies. In 2022, Lilley and Prasher1 proposed a way of generating cold based on another calorific effect. What they called the "ionocaloric refrigeration cycle" (see figure) describes the cooling and heating of a mixture of substances by changing the ion concentration with an accompanying phase change. It could be used as a thermodynamic cycle, for example in refrigeration systems for moderate cooling. It is based on lowering the melting point of an organic substance by adding a salt. In a circular process, the two substances would first be mixed to absorb heat and then separated again into the individual compounds to release heat during phase transformation (recrystallisation). Compared to conventional cooling systems such as compression chillers, ionocaloric cooling has the potential to be more efficient and environmentally friendly. This is due to the fact that it does not use ozone-depleting or climate-damaging refrigerants and does not require mechanical components such as compressors.
The research project initiated at the ILK Dresden aims to identify and qualify material pairs according to refrigeration technology criteria that are suitable for the ionocaloric circulation process and could be used in existing and new cooling applications. As part of the laboratory tests, the mixing temperatures of potentially suitable material mixtures are measured and the eutectic compositions are determined using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Another focus is the separation of the molten material mixtures into their components. To this end, suitable separation processes are selected and tested for their efficiency. In the context of a possible technical use, it is necessary to examine the materials for their corrosive behaviour towards the selected substances. Ionocaloric cooling in the circulation process poses a particular challenge for technical operation, as an answer must be found to the question of how the substances can best be transported in the liquid and solid aggregate state and how they can be mixed and separated most efficiently..
[1] Drew Lilley and Ravi Prasher: Supplementary Materials for Ionocaloric refrigeration cycle, Science 378, 1344 (2022)
Further Projects - Research and Development
Characterisation of Superconductors in Hydrogen Atmosphere
Are superconductors really compatible with hydrogen?
Development of a Cryogenic Magnetic Air Separation Unit
Oxygen Enrichment by Applied Cryogenic Magnetohydrodynamics